Context: To significantly reduce the cost of producing biodiesel, a multinational team of scientists from Assam, Odisha, China, and the UK has created a superhydrophobic catalyst. This catalyst offers significant cost savings and efficiency gains in the manufacture of biodiesel by replicating naturally occurring water-repellent surfaces like lotus leaves.
What is Biodiesel?
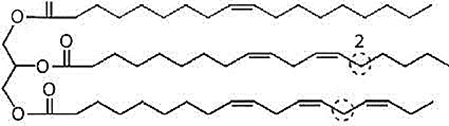
- In basic terms, oils produced from oilseeds are long straight chain hydrocarbons.
- The primary difference between diesel and biodiesel is this.
- Biodiesel is produced by breaking the long hydrocarbon straight chain in vegetable oil into 1/3rd, 1/3rd, and 1/3rd.
- In diesel-IC engines, biodiesel can be used in instead of diesel directly.
- Ester is the term for the biodiesel that is the end product.
- Because of this, the conversion of long, straight chain hydrocarbons into shorter chains is known as transesterification.
- One can break in the following ways:
- Heat it up: The process of Pyrolysis
- Put some force on it: Snapping
- Use hydrogen to replace double bonds: The process of hydrogenation.
For more : What is the concept of Nation and State?
What is Constitutionalism And Consitutional Morality
Feedstock for Biodiesel Production
- To extract oil, any oil seed can be utilized. However, using inedible oil seeds is a preferable choice.
- To make biodiesel, more than 200 different types of oil seeds can be utilized.
- Rice bran, sal, neem, mahua, karanja, castor, linseed, jatropha, honge, rubber seed, etc. are a few typical examples.
Advantages of Biodiesel
| Fuel | Energy density] (in MJ/ kg) |
| Ethanol | 24-25 |
| Petrol | 43-44 |
| Biodiesel | 40-41 |
| Diesel | 45.5 |
- High energy density
- Low energy input
- Nitrogen-fixation
- No Sulphur
- No aromatics
A case for biodiesel
- India consumes five times as much diesel as petrol, therefore finding a substitute for diesel is more crucial than finding one for petrol.
- Diesel de-sulfurization is an expensive process.
- Development of rural areas: raising crops based on oilseeds for biodiesel will increase farmer income.
- As leguminous crops, which aid in nitrogen fixation, make up the majority of oilseed crops, converting degraded land improves soil fertility.
Key Features of the Superhydrophobic Catalyst
- Innovation and Durability:
- The superhydrophobic catalyst has been engineered to endure the water byproduct generated during the manufacturing of biodiesel, retaining its high efficacy and permitting numerous applications. This invention is essential to improving the biodiesel manufacturing process’s efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
- Economic Impact:
- A litre of biodiesel now costs about $1.2. With the new catalyst, this price might drop to around 37 cents per liter, making biodiesel a more affordable option than regular diesel, which is currently priced at about ₹87 per liter in India.
- Advantages for the Environment and Economy:
- The catalyst is abundant and safe for the environment because it is made from biomass like cellulose. This strategy contributes to a cleaner future by lowering manufacturing costs and encouraging the use of renewable energy sources.
- More Wider Impacts:
- If this catalyst is successfully used, biodiesel may be used more widely, enhancing India’s energy security and lowering its reliance on fossil fuels.
Research and Development Contributions
- The National Institute of Technology (NIT) in Silchar, Assam; NIT Rourkela, Odisha; University of Cambridge; and Guizhou University, China were among the foreign universities that collaborated on the catalyst development. This demonstrates the value of international collaboration in the development of sustainable technology.
Technological Progress
- The catalyst makes use of biomass-derived activated carbon. This strategy makes the technology more widely available and economically viable by utilizing sustainable resources as well as offering an inexpensive substitute for pricey components like graphene and carbon nanotubes.
Prospects for the Future and Possible Uses
- The superhydrophobic catalyst may find use in coatings and filtration systems, among other applications where water-resistant materials are advantageous, in addition to the synthesis of biodiesel.
- Future cost reductions and efficiency gains may result from the research’s paving of the way for other breakthroughs in biofuel production.
Government Policies and Support
- National Policy on Biofuels (2018):
- Through a number of programs, the Indian government has been encouraging the development of biofuels. The National Policy on Biofuels (2018) encourages the development of biofuel in Export Oriented Units (EOUs) and Special Economic Zones (SEZs), permitting the unrestricted import of feedstock for export-oriented biofuel production.
- Targets and Amendments:
- The National Policy on Biofuels has recently been amended to allow for the development of biofuels from more feedstocks and to move forward the aim of 20% ethanol mix in gasoline to 2025–2026 from 2030. This is in line with the “Make in India” campaign, which seeks to promote domestic technical advancements, increase employment, and cut back on petroleum imports.
- Regulatory Framework:
- To guarantee that quality and quantity requirements are met, the Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas has released rules for the sale of biodiesel for blending with high-speed diesel. The integrity and dependability of the biodiesel industry depend heavily on this regulatory system.
Strategic Importance
- The National Policy on Biofuels, which aims to attain energy independence by 2047 as part of the Atmanirbhar Bharat (Self-reliant India) project, connects adoption of such technologies with India’s strategic goals.
- By tackling climate change, lowering greenhouse gas emissions, and encouraging cleaner, renewable energy sources, this invention also helps to achieve global environmental goals.
Conclusion
Superhydrophobic catalyst development is an important technical advance with broad economic and environmental applications in biodiesel synthesis. This invention, which is backed by strong legal and policy frameworks, is consistent with India’s objectives of economic expansion, sustainability, and energy security.
For more : Evolution of Judiciary During British Times

