The idea known as the Big Bang provides an explanation for the universe’s 13.7 billion-year evolutionary history.
Hubble’s Law and Expanding Universe
- Edwin Hubble significantly altered our perception of the nature of the universe in the 1920s.
- But until then, the common belief was that the universe is static and limitless. But Hubble proved a universe.
- This theory was expanded upon to account for the universe’s 13.7 billion-year evolutionary history.
Big Bang Theory

- According to Hubble’s law, the universe must have expanded in the past in order for it to be expanding now.
- Therefore, everything that exists in the universe today—matter, energy, and everything else—must have been compressed into a very tiny area at first, making it exceedingly dense. We refer to this as singularity.
- This incredibly dense primeval space started to expand 13.7 billion years ago, and it’s still expanding now.
- This is considered to be the beginning of the universe, and the Big Bang hypothesis explains it.
- The graphic and table below provide a brief overview of the universe’s development and significant turning points.
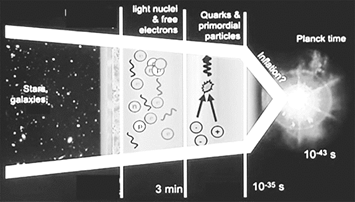
| Time since Big Bang | Event | Evidence | Observatories |
| t = 0-10-43s | Planks Time | We do not know | We do not know |
| t = 10-43s – 10-35s | Cosmic Inflation | Gravitational Waves?? | Gravitational Waves?? |
| t = 10-35s – 3 m | Quark confinement 1st Protons and Neutrons | Particle Accelerators | Large Hadron Collider (CERN), Tevitron, International Linear Collider (Japan?) |
| t = 3 m – 380000 years | Nucleosynthesis | Hydrogen and Helium filled universe | Spectral line of stars and galaxies |
| t = 380000 | Atomic synthesis | Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation | COBE, WMAP, BICEP 1 and 2 |
| t = 400 million years | 1st stars and Galaxies | Direct Observation | Telescopes |
For more :Catalytic Boost for Cheaper Biodiesel Production
Planck Time
- Impossible to know what happened.
- Laws of physics does not work in this phase.
Cosmic Inflation
- Not too long after the Planck time the universe saw a brief but extraordinarily fast expansion.
- It multiplied by around 1050 in all directions as it stretched outward.
- Recall that expansion refers to spatial expansion. Space expanded; particles did not flow through it.
- The universe cooled quickly as it expanded at such a phenomenal rate.
- The temperature dropped from 1032 Kelvin to 1027 Kelvin, creating an environment that was favorable for the formation of first matter.
- The universe’s temperature has decreased to 1015 K at t=10–12s.
Quark Confinement
- The fundamental components of all matter in the universe were generated during this time.
- Quark confinement is the method by which elementary particles, such as quarks (see Standard Model), came together to produce the first protons and neutrons.
- The formation of electrons and positrons occurred when the universe’s temperature dropped below 6 * 109 K, approximately one second ago.
Nucleosynthesis
- Protons and neutrons joined forces to form the first nucleus when the temperature dropped to around 4 *108 K. (This continued for 15 minutes.)
- Neutrons were unable to mix with protons after fifteen minutes. Neutrons decomposed into protons, electrons, and neutrinos as a result of this.
- No light could travel across the cosmos until t=380000 years ago because high-energy photons were interacting with protons, neutrons, electrons, and other matter particles.
- We claim that the cosmos was opaque up to this point.
Atomic Synthesis And Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation
- High-energy photons ceased interacting with protons, electrons, and other matter particles around t=380000, when temperatures had dropped to roughly 3000K. This created an environment that was favorable for electrons to bond to nuclei and form the first atoms.
- Prior to this, high-energy photons that prohibited electrons from binding to nuclei made up the universe’s radiation.
- Hydrogen was the predominant atom producing.
- Furthermore, helium atoms were being formed by the fusion of hydrogen atoms. (like what occurs in the sun now)
- It would be equivalent to declaring that the entire universe was a sun, radiating visible light in the same manner as our sun does now.
- The emission of visible light permeated the entire cosmos. The visible light in the cosmos is expanding together with it, turning into microwave radiation. Cosmic microwave background radiation is what happens when light is stretched, increasing its wavelength and turning visible light into microwave radiation.
Nonuniformities In The Early Universe And The Origin Of Galaxies
- As we have seen, the first atoms formed around 380000 years ago. Matter that was creating clumped together because of gravity as the cosmos expanded. As a result, the cosmos is not uniform, with some regions having a lot of matter and others having none.
- Approximately 400 million years ago, the universe’s first galaxies formed due to the accumulation of so much stuff in one place.
- Even now, the cosmos is characterized by this non-uniformity in the existence of matter. Because of its gravitational pull to one another, matter tends to cluster together, exhibiting nonuniformity. (The force of gravity attracts any two bodies having mass.)
- The universe’s many formations are the result of stuff congealing together.Gravity not only causes objects to cluster together but also gives the universe a hierarchical structure.
- As a result, stars aggregate to create galaxies, which then aggregate into clusters (local groups), clusters of galaxies combine to form superclusters, and so on.
- Clusters of 10–10,000 galaxies that are gravitationally bound contain the majority of galaxies.
For more : What is the concept of Nation and State?
