Introduction to Industrial Revolution 4.0
The Industrial Revolution 4.0, often referred to as Industry 4.0, represents a profound transformation of the way we live and work, driven by the integration of digital technologies, data, and automation into various industries.
It stands as the latest chapter in the ongoing history of industrialization, promising to reshape economies, societies, and the very nature of work itself. This essay explores the key aspects and implications of Industrial revolution 4.0
- The World Economic Forum (WEF) has chosen Hyderabad for establishing its Centre for the Fourth Industrial Revolution focused on healthcare and life sciences. India becomes the fourth country to have such a centre after US, Japan and China.
- C4IR Telangana will be the 18th centre to join WEF’s Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR) network that spans four continents.

The Foundations of Industry 4.0
- Technological Advancements: Industrial revolution 4.0 is underpinned by a constellation of technologies, including artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), big data analytics, robotics, 3D printing, and blockchain. These technologies have reached a level of maturity that allows them to be seamlessly integrated into industrial processes.
- Data as the New Currency: Data is at the heart of Industry Industrial revolution 4.0. The ability to collect, analyze, and leverage vast amounts of data in real-time is revolutionizing decision-making and optimizing processes across industries.
- Interconnectivity: IoT connects devices, machines, and systems, enabling real-time communication and coordination. This interconnectivity forms the backbone of smart factories and supply chains, increasing efficiency and responsiveness.
History of the Industrial Revolution
- The First Industrial Revolution used water and steam power to mechanize production. It was the first instance where production shifted from cottage industry to large production houses or factories.
- The Second industrial revolution used electric power for mass production. That is, large scale machines were brought into the picture. Huge conveyor belts rolling products one after the other, automobiles and production of electricity, defined this phase.
- The discovery of computers laid the path for the third revolution. The third phase was the most important as the machines which previously were electrically driven became electronically driven, that is, it used electronics and information technology to automate production. This came around in the middle of the 20th century.
- It is seen that each revolution took about a hundred years to establish and then give way to the next revolution.
- Now a Industrial revolution 4.0 is building on the third revolution, that is, the digital revolution that has been occurring since the middle of the last century. It is characterized by a fusion of technologies that is blurring the lines between the physical, digital and biological spheres.
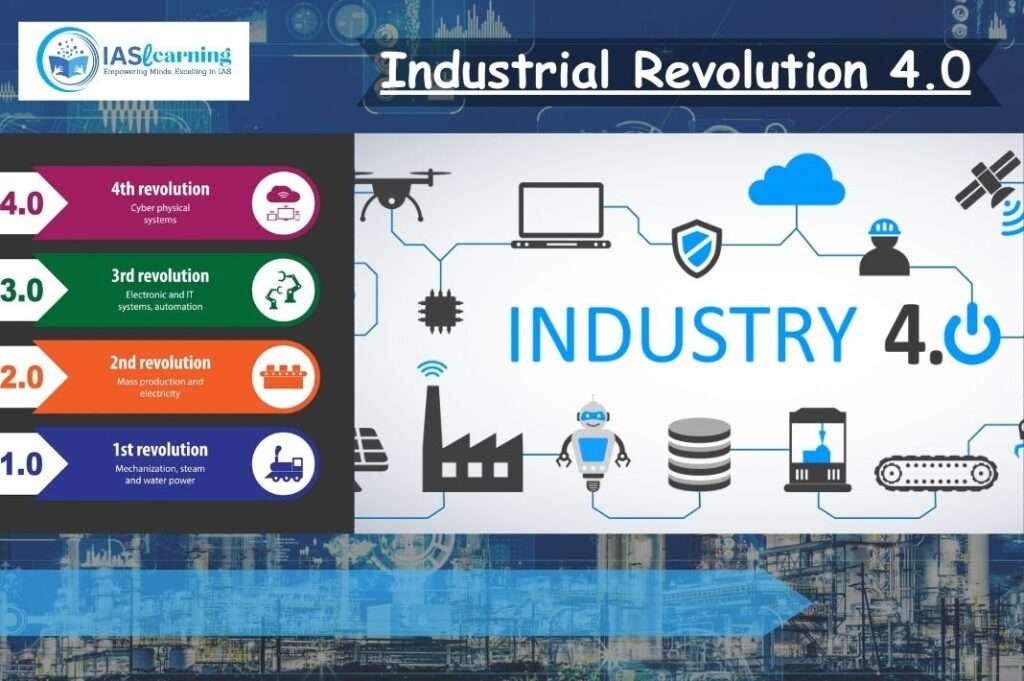
Industrial revolution 4.0
- The Industrial revolution 4.0 is a term that describes present technological age. It is the fourth industrial era since the inception of the initial Industrial Revolution of the 18th century. The key elements of the fourth revolution are the fusion of technologies ranging from the physical, digital to biological spheres.
- Building on the foundation given by the third Industrial Revolution, the fourth Industrial Revolution is moving from an electronic based industry to a process which is the combination of human beings and electronics.
- It includes cyber-physical systems, the Internet of things, big data analytics, cloud computing, cognitive computing, artificial intelligence, 3-D printing, autonomous vehicles etc.
- The best example would be processed artificial intelligence, has broken breaking the distinction between the Man, the Machine and Intelligence.
Impact of Industrial revolution 4.0
- Services and business models improvement.
- Reliability and continuous productivity.
- IT security and better resource utilization.
- Machine safety and better working condition.

Key Aspects of Industrial revolution 4.0
- Smart Manufacturing: In Industrial revolution 4.0 factories become smart. Machines communicate with each other, and production processes are optimized in real-time, leading to increased productivity and reduced waste. Predictive maintenance ensures machines are serviced before they break down, minimizing downtime.
- Digital Twins: Digital twin technology creates virtual replicas of physical systems, allowing for simulations and testing before implementing changes or improvements in the real world. This reduces risks and accelerates innovation.
- Decentralized Manufacturing: 3D printing and distributed manufacturing are making it possible to produce goods closer to consumers, reducing shipping costs and environmental impact.
- AI and Automation: AI-powered robots and systems are increasingly taking on repetitive tasks, while humans focus on creative, decision-making, and value-added activities. This enhances efficiency and reduces errors.
- Supply Chain Transformation: Smart logistics and supply chains optimize routes, manage inventory more efficiently, and provide real-time tracking. Blockchain ensures transparency and security in the supply chain.
Technologies of the Industrial revolution 4.0
- Artificial Intelligence: AI defines computers that can think like humans. With the help of AI computer can recognize complex patterns, process information, draw conclusions and make recommendations. AI has many applications, from spotting patterns in huge piles of unstructured data to powering the autocorrect on your our phone, to the smallest chip to a big manufacturing process.

- Blockchain: It is a secure, decentralized, and transparent way of recording and sharing data and it does not depend on any third-party intermediaries. Bitcoin is a digital currency which is the best-known blockchain application. However, the technology has other applications like traceable supply chains, securing sensitive medical data anonymously and combating voter fraud.
- Cloud Computing: New computational technologies are making computers smarter as they can process vast amounts of data faster than ever before. The advent of the cloud has allowed businesses to safely store and access their information from anywhere with internet access.
- Quantum Computing: It will eventually make computers millions of times more powerful. These computers will have the potential to enhance AI, create highly complex data models in seconds and speed up the discovery of new materials.
- Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality: Virtual Reality (VR) offers immersive digital experiences (using a VR headset) that simulate the real world, while augmented reality (AR) combined the digital and physical worlds. Examples include makeup apps, which allow users to digitally experiment with makeup products before buying them, and the For example, Google Translate phone app, which allows users to scan and instantly translate street signs, menus, and other text.
- Biotechnology: It utilizes cellular and biomolecular processes to develop new technologies and products for developing new pharmaceuticals and materials, efficient industrial manufacturing processes, cleaner, more efficient energy sources, etc. Another example is our ability to edit the blocks of life has recently been massively expanded by low-cost gene sequencing and techniques such as CRISPR, stem cell technology, mRNA vaccine, etc.
- Robotics: It refers to the design, manufacture, and use of robots for personal and commercial use. While the use of robot assistants in every home is still to be a reality, technological advances have made robots increasingly complex and sophisticated. They are used in fields as wide-ranging as manufacturing, health, safety and human assistance.
- The Internet of Things: The IoT describes everyday items from medical wearables that monitor users’ physical condition to cars and tracking devices inserted into parcels connected to the internet and identifiable by other devices. Businesses can collect customer data from constantly connected products, allowing them to better gauge how customers use products and tailor marketing campaigns accordingly. There are also many industrial applications, such as farmers putting IoT sensors into fields to monitor soil attributes and inform decisions such as when to fertilize.
- 3D Printing: It allows manufacturing businesses to print their parts, with less tooling, at a lower cost, and faster than via traditional processes. Designs can be customized to ensure a perfect fit.

Industrial Revolution 4.0 in Socio-economic Development
- It can play a major role in alleviating poverty. Better and low-cost health care can be achieved through the implementation of AI driven diagnostics, personalized treatment, early identification of potential pandemics and imaging diagnostics, among others.
- Enhancing farmer’s income by providing them with the latest technologies, improvement in crop yield through real-time advisory, advanced detection of pest attacks, and prediction of crop prices to inform sowing practices.
- It will strengthen infrastructure and improve connectivity to the very last village. Artificial intelligence can be used to empower and enable specially-abled people.
- It will improve ease of living and ease of doing business using smart technologies.
- Recently, India has announced her drone policy, which will play an important role in security traffic and mapping.
Status of Industrial revolution 4.0 in India
- India is moving towards becoming a hub of global manufacturing, 3D printing, machine learning, data analytics, and IoT are key to promoting industrial growth,
- In November 2020, the Modern Coach Factory (MCF) at Raebareli, Uttar Pradesh, rolled out smart railway coaches that are fitted with a battery of sensors to provide a comfortable experience to passengers.
- In May 2020, the Union Ministry of Heavy Industries launched the Smart Advanced Manufacturing and Rapid Transformation Hub (SAMARTH) scheme, which brings together manufacturers, vendors, and customers to make them aware of Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR) technologies.
- In 2022’s budget speech, the Union finance minister announced a slew of new 4IR-driven projects, including Drone Shakti, to encourage start-ups that will facilitate the use of drone services.
- India even has a 4IR centre in Mumbai run by WEF, which is closely working with several state governments.
- The Centre has recently come up with the Fourth Industrial Revolution for Sustainable Transformation (FIRST) Cancer Care model in which 4IR technologies would be used to provide better healthcare for cancer patients
- In February 2022, Government launched the pan-India 3D maps programme by Genesys International for the 100 smart cities. The company plans to map an entire city in intricate detail so that many 4IR revolution technology-based projects, such as driverless cars, will become easier to implement.
- National Programme on AI (NPAI): Envisioned as an umbrella programme by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology for leveraging transformative technologies to foster inclusion, innovation, and adoption for social impact. Consequently, INDIAai (The National AI Portal of India) is poised to assume the pivotal role of a content repository for The National Program on AI. Six major NPAI pillars are:
- AI in Governance
- AI IP and Innovation
- AI Compute and System
- Data for AI
- Skilling in AI
- AI Ethics and Governance
Challenges
- Inequality: The revolution could yield greater inequality, particularly in its potential to disrupt labour markets. As automation substitutes for labour across the entire economy, the net displacement of workers by machines might exacerbate the gap between returns to capital and returns to labour.
- Inequality represents the greatest societal concern associated with the Fourth Industrial Revolution. The gap between those dependent on capital and labour will increase.
- Unemployment: The immediate fear of technology is job loss, particularly in informal sector. Technology is one of the main reasons why incomes have stagnated or decreased. For a majority of the population in high-income countries- the demand for highly skilled workers has increased while the demand for workers with less education and lower skills has decreased.
- Threat to Privacy: One of the greatest individual challenges posed by new information technologies is privacy. More than 30 percent of the global population uses social media platforms.
- This can also create and propagate unrealistic expectations as to what constitutes success for an individual or a group, as well as offer opportunities for extreme ideas and ideologies to spread.
- Policymaking: Current systems of public policy and decision-making evolved alongside the Second Industrial Revolution. But the rapid changes of the fourth revolution demands broader regulations with the inclusiveness of customers, developers, and the public at large.
- Security Threat: It will also profoundly impact the nature of national and international security, affecting both the probability and the nature of the conflict. This will lead to new fears.
- New technologies such as autonomous or biological weapons become easier to use, individuals and small groups will increasingly join states in being capable of causing mass harm.
OR
Coupled with the promise that 1 4.0 offers, there are challenges as have been seen and reported in various contexts. These can be divided in following four categories;
- Economic
- High economic cost of implementation
- Adoption of new business model
- Integration of pre-existing systems (CAD, CAM, MES, PLM)
- Ambiguous economic benefits
- Social
- Privacy concerns
- Surveillance and distrust
- General reluctance to change
- Threat of redundancy of Corp IT projects
- Loss of (low end) jobs
- Lack of required skills
- Political
- Lack of Regulations
- Unclear Legal issues
- Lack of appetite to change
- Organizational
- Security of data
- Reliability & scalability
- Low management support
- Insufficient experience
- Integrity of Processes
- Risk of investment paying back
Way Forward
- Industrial revolution 4.0 has started to make an influence in manufacturing and other various sectors in India.
- Data-driven decision-making is getting implemented in numerous fields.
- Though certain steps have already been taken, a lot of work needs to be done.
- Instead of just spending more capital, the emphasis must be on increasing the current asset base.
- The implementation of smart manufacturing, data analytics, and the Internet of Things will give a positive direction to Indian industries.
- To secure India’s active involvement in the fourth industrial revolution, it will be necessary to restructure some vital domestic industries and strengthen institutional capability.
Conclusion
Industrial revolution 4.0 is more than just a technological shift; it’s a fundamental transformation that has the potential to reshape economies, industries, and societies worldwide. While it offers tremendous opportunities for increased efficiency, productivity, and sustainability, it also presents challenges, particularly regarding workforce adaptation and the ethical use of technology. As we navigate this fourth industrial revolution, it is crucial to strike a balance between innovation and responsibility, ensuring that the benefits of Industrial revolution 4.0 are widely shared and that it serves as a force for positive change in the world.
Read Morehttps://www.mckinsey.com/
Do Followhttps://iaslearning.in/

