Frustration Mounts in Israel-Palestine Relations
Table of Contents
Context to Israel-Palestine conflict
The two-state solution to the Israel-Palestine conflict, which envisions the creation of two separate and independent states for Israelis and Palestinians, has been considered the most viable long-term solution since the beginning of the Jewish-Arab conflict in the region. This approach aims to divide the land between the Jordan River and the Mediterranean Sea, providing both Israelis and Palestinians with their own sovereign nations.
The Gaza-Israel conflict is a localized aspect of the broader Israeli-Palestinian conflict. It began with the election of the Islamist political party Hamas in 2005 and 2006 in the Gaza Strip. The conflict escalated as a result of the division of the Palestinian Authority into the Fatah government in the West Bank and the Hamas government in Gaza. This division led to violent confrontations, particularly after Hamas won the election.
The conflict involves Palestinian rocket attacks on Israel, Israeli airstrikes on Gaza, and a joint Egyptian-Israeli blockade of Gaza. These actions have worsened the conflict. It’s important to note that the international community views attacks on civilians and civilian structures, especially when there’s no distinction between civilians and military targets, as illegal under international law.

Historical Background:
- The historical background of the Israel-Palestine conflict is marked by both Arabs and Jews having deep-rooted self-conceptions of nationhood tied to the same land. However, over the course of the conflict, there has been a shift in perspectives. Initially, Jews accepted the inevitability of partition, while many Arabs rejected it. In recent decades, this situation seems to have reversed.
- Today, a significant portion of the Palestinian leadership, along with much of the Arab world and Western nations, support the idea of a two-state solution, where a sovereign Palestinian state would exist in the West Bank and Gaza, with its capital in East Jerusalem. However, it is Israel that has been hesitant to move forward with the establishment of such a state.
- Understanding the reasons behind Israel’s reluctance is crucial for predicting the consequences of recent events, including Hamas’s terror attacks on Israel, which have resulted in casualties on both sides and have provoked an Israeli response.
Creation of Israel:
- In 1947, the United Nations approved a plan to partition Palestine into separate Jewish and Arab states, with Jerusalem as an international city. Israel declared its independence in 1948.
- Arab states rejected the partition plan, leading to the Arab-Israeli War of 1948-1949 (also known as the War of Independence), resulting in Israel’s establishment and displacement of Palestinian Arabs.
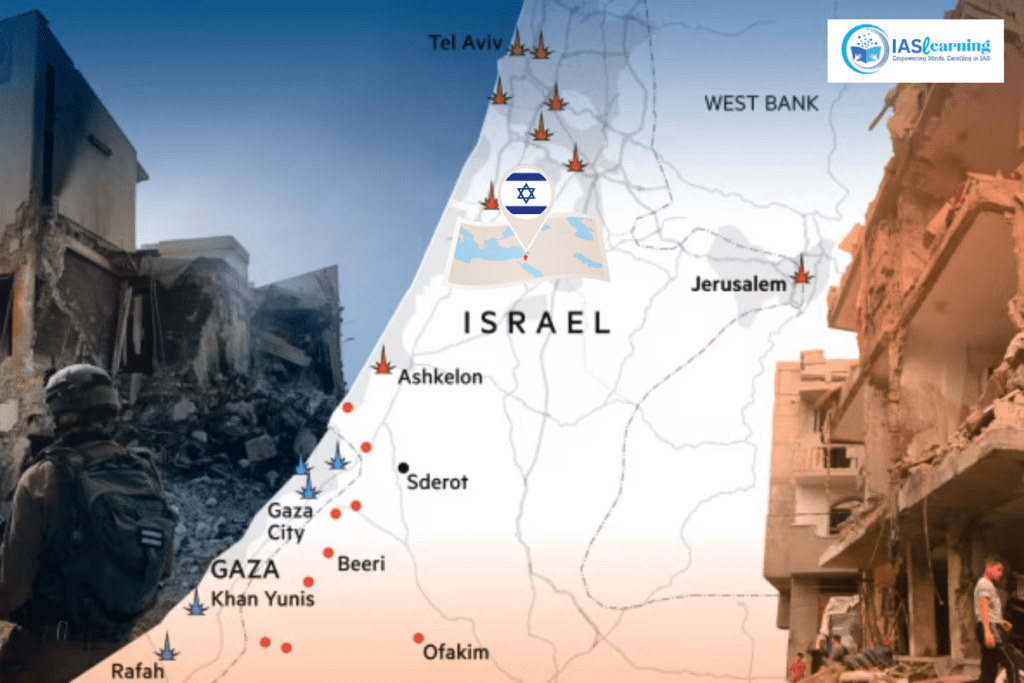
Gaza Strip:
- The Gaza Strip, a small coastal enclave, came under Egyptian administration following the 1948 war. It was occupied by Israel during the Six-Day War in 1967.
- Israel withdrew its settlers and military forces from Gaza in 2005 but maintained control over its borders, airspace, and coastline, leading to a state of limited autonomy for the Palestinian Authority in Gaza.
Hamas:
- In 2006, the Palestinian elections saw the victory of Hamas, a Palestinian Islamist organization considered a terrorist group by Israel and some Western countries.
- This led to political tensions between the Palestinian Authority, which controlled the West Bank, and Hamas, which controlled Gaza.
Ongoing Conflict:
- The Israel-Gaza conflict has witnessed several military conflicts, with Israel launching operations in response to rocket attacks from Gaza and Hamas firing rockets into Israeli territory.
- These conflicts have resulted in significant civilian casualties on both sides, drawing international attention and condemnation.
Ceasefires and Peace Efforts:
- International efforts, including multiple ceasefires brokered by Egypt, the United Nations, and other mediators, have been attempted to reduce violence and reach a lasting resolution.
- However, a comprehensive peace agreement remains elusive, with core issues such as borders, refugees, Jerusalem, and the status of Palestinian territories still unresolved.
Stakeholders

- In the Israel-Palestine conflict, the real stakeholders can be viewed from both a perspective of justice and realpolitik. From a standpoint of justice, the primary stakeholders are the Palestinian and Israeli people. However, in terms of realpolitik, the key stakeholder has historically been the Israeli public. This is because Israel’s agreement and acquiescence are crucial for any potential solution, and since Israel is a democracy, the public’s opinion holds significant weight.
- The central question is whether Hamas’s recent attacks will push the Israeli public toward the creation of a sovereign Palestinian state. Some opinion makers believe that the trauma caused by these attacks may lead Israelis to recognize the necessity of a Palestinian state for achieving peace.
- However, there is an alternative viewpoint, which suggests that Israelis may reach the opposite conclusion. They may fear that a two-state solution, where a sovereign Palestinian state has its own army and security apparatus, could empower Palestinians to launch more effective attacks on Israel. The concern is that an independent Palestine might follow a similar path to Hamas in terms of hostilities.
Hamas’s stance
- Hamas’s stance in the Israel-Palestine conflict is marked by its refusal to accept Israel’s right to exist in any form. It has carried out attacks on Israel’s southern borders, including areas that would likely remain with Israel in any potential peace agreement. These attacks have resulted in the killing and abduction of innocent civilians, rather than targeting religious settlers in the West Bank.
- The fact that the Palestinian Authority in the West Bank has supported Hamas’s actions adds to Israeli concerns. Instead of envisioning a scenario where a Palestinian and Jewish state coexist side by side, Israelis fear that the outcome may be a single Palestinian state encompassing the entire territory between the Jordan River and the Mediterranean Sea.
- The primary obstacle to a two-state solution, therefore, has not solely been the Israeli occupation of the West Bank and Gaza, but the challenge of convincing Israeli voters that granting sovereignty to Palestinians in one part of the land would lead to peaceful coexistence. While there has always been a fringe of radical Israelis opposed to the idea of Palestinians having their own state, these views have gained more prominence in Israeli politics today. This shift reflects a growing distrust among Israeli voters regarding Palestinians as potential partners in a future peace agreement.
Way Forward
- The Israel-Palestine conflict has taught Palestinians that sharing their pain with Israeli civilians is a strategy to compel a reduction in their suffering. However, from the Israeli perspective, each wave of violence against their civilian population has made them less inclined to take the risk of ending the occupation of Palestinians.
- Given the substantial power imbalance between Israel and the broader Arab world, the most viable path for Palestinians to achieve their sovereign state is by convincing Israeli voters that a future Palestine will coexist peacefully with Israel.
- Moving forward, the key lies in Palestinian leadership that can convincingly communicate to the Israeli people that any freedoms gained from a peace agreement will not be used to harm Israel. Unfortunately, the prospects for such leadership appear challenging at present.

