Introduction to Poverty in India
India, a land of diversity and contrasts, is not only known for its rich culture and heritage but also for its persistent issues related to poverty, inequality, and unemployment. In this article, we will delve deep into the intricate web of these challenges that continue to affect millions of lives in the country. By examining the data, we aim to shed light on the root causes, consequences, and potential solutions to address these pressing concerns.
Statistics
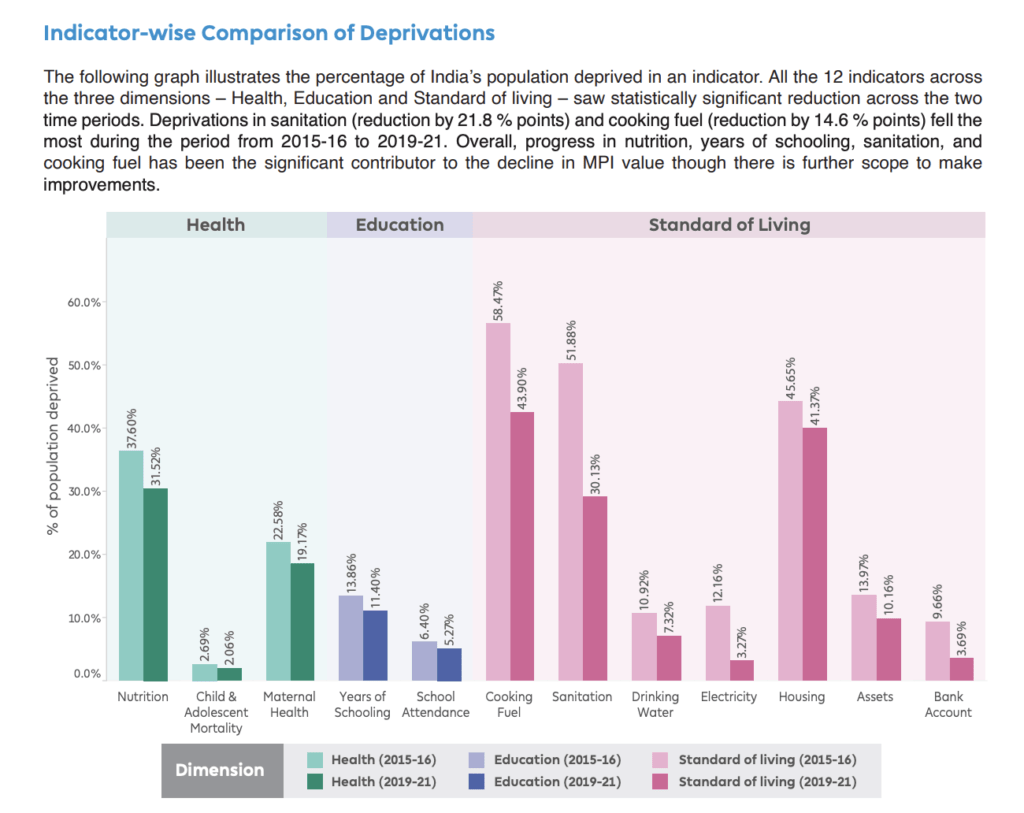
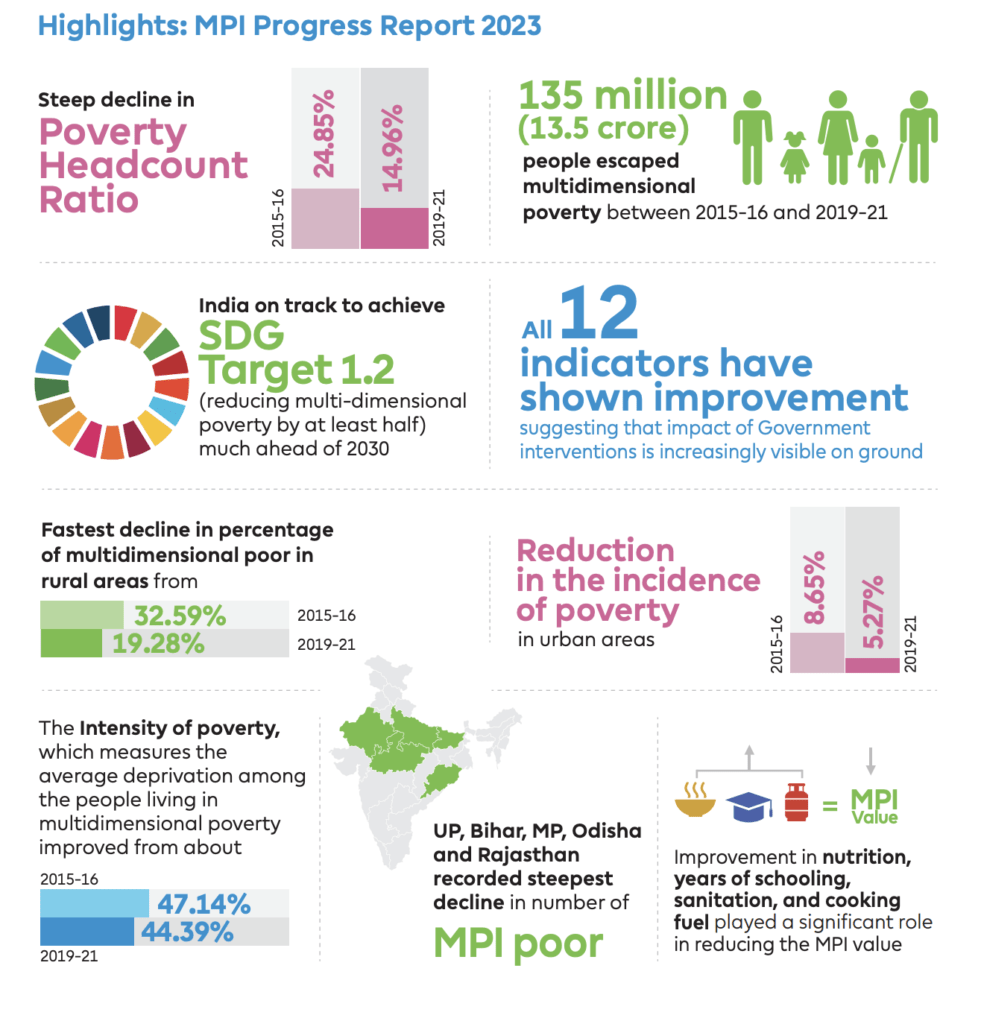
According to the Report, 135 million people escaped multidimensional poverty between 2015-16 and 2019-21. The country registered a significant decline of 9.89 percentage points in India’s multidimensionally poor from 24.85% in 2015-16 to 14.96% in 2019-2021. The rural areas witnessed the fastest decline in poverty, from 32.59% to 19.28%.
The Three Pillars of Indian Socioeconomic Challenges
1. Poverty in India: A Harsh Reality
India is home to a significant portion of the world’s poor population. Despite remarkable economic growth over the past few decades, poverty remains a pervasive issue. The data paints a grim picture, showing that a large segment of the population still lives below the poverty line.
2. Income Inequality: The Growing Gulf
Income inequality is another pressing concern. As India’s economy grows, the gap between the rich and the poor continues to widen. This trend raises questions about the distribution of wealth and opportunities in the country.
3. Unemployment Crisis: Youth at Crossroads
With a growing population and limited job opportunities, unemployment has become a significant challenge, particularly for the youth. Understanding the data on unemployment rates is crucial to address this issue effectively.
Poverty in India: A Closer Look
1. Definition and Measurement
Before diving into the data, let’s understand how poverty is defined and measured in India. The poverty line is determined based on income levels and the ability to afford basic necessities such as food, shelter, and healthcare.
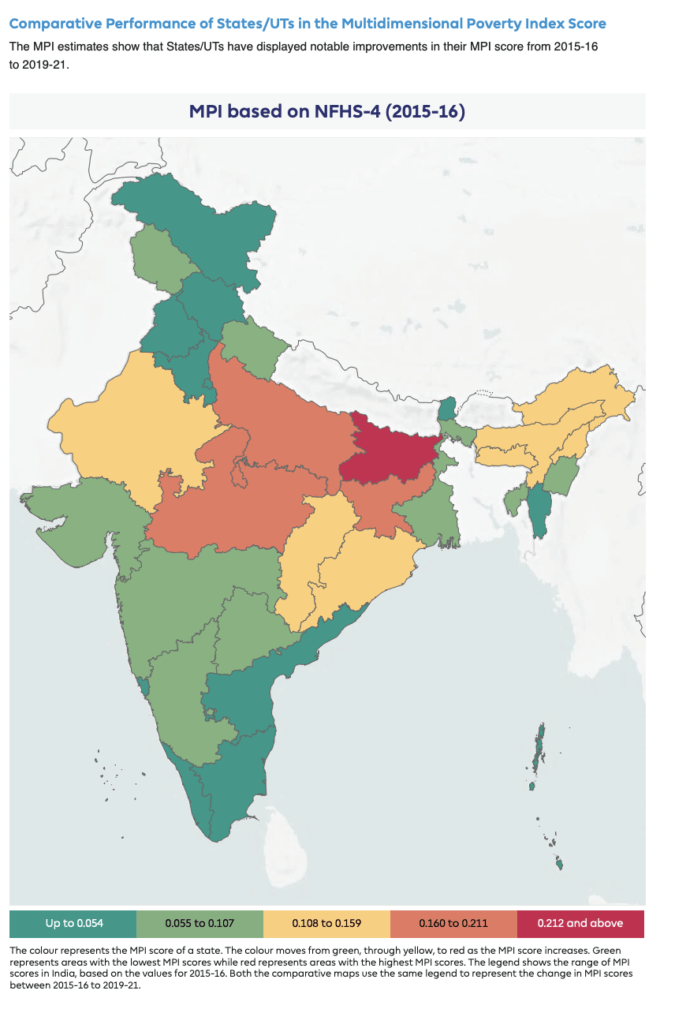
2. Regional Disparities

One striking aspect of poverty in India is the significant regional disparities. While some states have made significant progress in poverty reduction, others continue to grapple with high poverty rates. Analyzing these disparities can provide valuable insights into targeted interventions.
3. Rural vs. Urban Poverty
The rural-urban divide plays a crucial role in understanding poverty in India. Data shows that rural areas tend to have higher poverty rates compared to urban areas. Factors like limited access to education and healthcare contribute to this disparity.
Income Inequality: The Widening Gap
1. The Gini Coefficient
To quantify income inequality, economists often refer to the Gini coefficient. The data reveals a concerning trend as this coefficient continues to rise in India, indicating an increasingly unequal distribution of income.
2. Causes of Income Inequality
Understanding the root causes of income inequality is essential. Factors such as unequal access to education and employment opportunities, as well as discrimination based on caste and gender, contribute to this issue.
3. Impacts on Society

Income inequality has far-reaching consequences, affecting not only economic stability but also social cohesion. High levels of inequality can lead to unrest and social unrest, making it imperative to address this issue promptly.
The Unemployment Crisis: A Growing Concern
1. Youth Unemployment
Youth unemployment is a matter of great concern in India. With a burgeoning young population, the inability to provide gainful employment can have severe repercussions. Examining data on youth unemployment rates is essential.
2. Skill Mismatch
One key factor contributing to unemployment is the mismatch between the skills possessed by job seekers and the skills demanded by the job market. Bridging this gap is crucial for reducing unemployment rates.
3. Government Initiatives to eradicate Poverty in India

Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA): This flagship program guarantees 100 days of wage employment to every rural household in India, with the objective of enhancing livelihood security in rural areas. It provides employment opportunities to those living below the poverty line and helps reduce seasonal unemployment.
Pradhan Mantri Awaas Yojana (PMAY): The PMAY program aims to provide affordable housing to the rural and urban poor. It includes schemes like “Housing for All” that focus on building houses for economically disadvantaged families, ultimately improving their quality of life.
National Rural Livelihood Mission (NRLM): NRLM, also known as Aajeevika, focuses on promoting self-employment and entrepreneurship among rural poor households. It provides financial support, skill training, and access to credit to help individuals and self-help groups (SHGs) generate sustainable income.
National Food Security Act (NFSA): NFSA aims to provide food security to vulnerable populations by subsidizing food grains under the Public Distribution System (PDS). It ensures that eligible families receive essential food items at affordable prices.
Deen Dayal Upadhyaya Antyodaya Yojana (DAY-NRLM): DAY-NRLM is designed to uplift the rural poor by creating sustainable livelihood opportunities. It focuses on empowering women through self-help groups and community-based initiatives.
Swachh Bharat Abhiyan (Clean India Campaign): While not exclusively an anti-poverty program, Swachh Bharat Abhiyan addresses sanitation and hygiene issues, which are critical for improving the health and well-being of impoverished communities.
Rural and Urban Housing Schemes: Various state and central government schemes provide financial assistance and subsidies for constructing and upgrading housing for the poor in both rural and urban areas.
Jan Dhan Yojana: This financial inclusion program aims to provide access to banking and financial services to all citizens, particularly those from economically disadvantaged backgrounds. It encourages savings and enables access to credit and insurance.
Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY): PMKVY focuses on skill development and vocational training to enhance employability. It targets youth, including those from low-income families, and equips them with industry-relevant skills.
National Rural Health Mission (NRHM): NRHM aims to improve the healthcare infrastructure and accessibility of healthcare services in rural areas, ensuring that even the poorest citizens have access to quality healthcare.
Conclusion to Poverty in India
In conclusion, the data on poverty, inequality, and unemployment in India highlights the multifaceted challenges that the nation faces. Addressing these issues requires a comprehensive approach that takes into account regional disparities, income inequality, and the youth unemployment crisis. It is crucial for policymakers, researchers, and civil society to work collaboratively to develop and implement effective solutions.
FAQs
1. What is the poverty line in India?
The poverty line in India is determined based on income levels and the ability to afford basic necessities such as food, shelter, and healthcare. It varies by region and is periodically updated.
2. How does poverty in India impact society?
Income inequality can lead to economic instability and social unrest. It hampers social cohesion and can result in disparities in access to essential services and opportunities.
3. What government initiatives are in place to address poverty in India?
The Indian government has introduced various schemes and programs, such as “Make in India” and “Skill India,” to combat unemployment and promote skill development.
4. What are the key factors contributing to youth unemployment in India?
Youth unemployment in India can be attributed to factors like skill mismatch, limited job opportunities, and lack of access to quality education and vocational training.
5. How can individuals contribute to addressing these challenges?
Individuals can contribute by supporting organizations working on poverty alleviation, advocating for policies that promote income equality, and participating in skill development programs to enhance employability.
Read more….https://iaslearning.in/rajasthan/




