Introduction: Shanghai Cooperation Organisation
- The Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) is a Eurasian political, economic, and security alliance established in 2001.
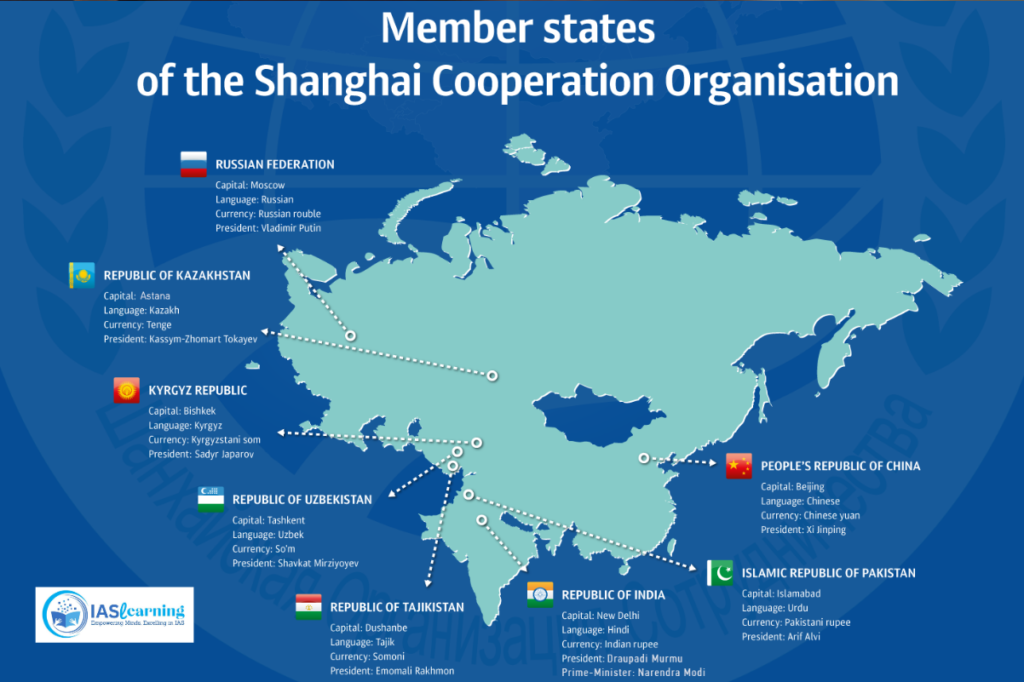
- Initially founded by China, Russia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan, it has expanded its membership since then.
Member States of Shanghai Cooperation Organisation
- Founding Members: China, Russia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan.
- India and Pakistan joined as full members in 2017, expanding the organization’s reach to South Asia.
Objectives of Shanghai Cooperation Organisation
- Enhance political, economic, and cultural cooperation among member states.
- Foster regional stability and security.
- Counter-terrorism and extremism.
- Facilitate trade and economic cooperation.
Institutions within Shanghai Cooperation Organisation :
- SCO Summit: Heads of State meetings to discuss and decide on major issues.
- SCO Council of Ministers: Addresses issues of mutual interest and sets the agenda for the organization.
- SCO Regional Anti-Terrorist Structure (RATS): Coordinates efforts against terrorism, separatism, and extremism.
- SCO Business Council and Interbank Consortium: Promotes economic cooperation and development.
India’s Role:
- India’s inclusion in the SCO provides it with a platform to engage more deeply with Central Asian countries.
- Cooperation in the fields of counter-terrorism, energy, and trade.

Challenges and Concerns:
- Divergent interests among member states.
- Managing regional conflicts and historical disputes.
Significance for UPSC:
- The SCO is crucial for understanding India’s foreign policy and its engagement with Central Asian countries.
- It reflects India’s efforts to enhance its strategic and economic ties beyond South Asia
Areas of Cooperation:
Security Cooperation: The SCO has a strong focus on regional security, particularly in combating terrorism, separatism, and extremism. Member states conduct joint military exercises and share intelligence to address common security threats.
Economic Cooperation: The organisation aims to promote economic development and cooperation among member states. Initiatives include the development of transport infrastructure, trade facilitation, and joint projects in areas such as energy and technology.
Cultural and Educational Exchanges: The SCO encourages cultural and educational cooperation to foster mutual understanding among member states. This includes initiatives to promote language learning, academic exchanges, and cultural events.

Connectivity Initiatives:
The SCO emphasises the importance of connectivity in the region. Efforts include enhancing transportation links, developing transit corridors, and improving digital connectivity. These initiatives aim to boost economic cooperation and people-to-people ties.
Observer States and Dialogue Partners:
Besides full members, the SCO has observer states and dialogue partners. Iran is one of the observer states, and Afghanistan is a dialogue partner. These relationships expand the SCO’s influence and engagement beyond its core membership.
Challenges in Regional Security:
The SCO faces challenges in addressing complex regional security issues, including the situation in Afghanistan, which has implications for the stability of Central Asia. Understanding how the organization responds to such challenges is crucial for a comprehensive understanding.
Belt and Road Initiative (BRI):
China’s Belt and Road Initiative, a massive infrastructure and economic development project, aligns with the SCO’s goals. The synergy between the SCO and BRI is noteworthy, and candidates should be aware of how these initiatives intersect and influence regional dynamics.
Role of the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation in Resolving Regional Conflicts:
The organization plays a role in mediating and resolving disputes among member states. Understanding its conflict resolution mechanisms and their effectiveness is vital for analyzing the impact of the SCO on regional stability.
Post-Soviet Space and SCO:

The SCO’s engagement with Central Asian states, many of which were part of the Soviet Union, provides insights into the evolving dynamics in the post-Soviet space. This is particularly relevant for understanding the historical and geopolitical context of the region.
Global and Regional Impact:
The SCO’s increasing relevance on the global stage, especially in the context of shifting geopolitical dynamics, is a subject of interest. Analyzing how the SCO contributes to shaping regional and global affairs adds depth to one’s understanding.
Future Prospects:
Anticipating the future direction of the SCO, its potential challenges, and its role in emerging global scenarios is crucial for aspirants preparing for the UPSC exam.
Remember to integrate current developments and news related to the SCO into your preparation, as this will provide a more comprehensive understanding of its evolving role in international relations.

